When looking at verapamil, a prescription calcium‑channel blocker that relaxes heart muscle and blood vessels, you quickly see why doctors rely on it for several heart conditions. It works by blocking calcium entry into cardiac cells, which slows the heart rate and lowers blood pressure. Because of this dual action, it’s a go‑to option for high blood pressure, chest pain from reduced blood flow, and certain rhythm problems. People often ask if it’s safe with other meds – the answer hinges on understanding its interactions and side‑effect profile.
The effectiveness of calcium channel blockers, drug class that includes verapamil, diltiazem and amlodipine depends on how they target the heart’s electrical activity. Hypertension, a chronic condition marked by elevated arterial pressure is one of the most common reasons doctors prescribe this class, because lowering pressure reduces strain on arteries and the risk of stroke. When angina, chest pain caused by insufficient blood flow to the heart muscle spikes during exertion, verapamil’s ability to widen coronary vessels can ease symptoms and improve exercise tolerance. The drug also finds a place in managing irregular heartbeats such as atrial fibrillation, where slowing conduction helps restore a normal rhythm. These entities intersect: calcium channel blockers treat hypertension, hypertension raises the chance of angina, and angina often coexists with rhythm disorders. Understanding these links helps you see why a single medication can address multiple cardiac issues.
Below you’ll find a curated collection of articles that break down verapamil’s role alongside other popular heart drugs. We compare dosing, side effects, cost, and the situations where verapamil shines or where an alternative might be better. Whether you’re a patient looking for clear guidance or a health‑care professional needing a quick refresher, the posts ahead give practical, up‑to‑date insights you can act on right away.
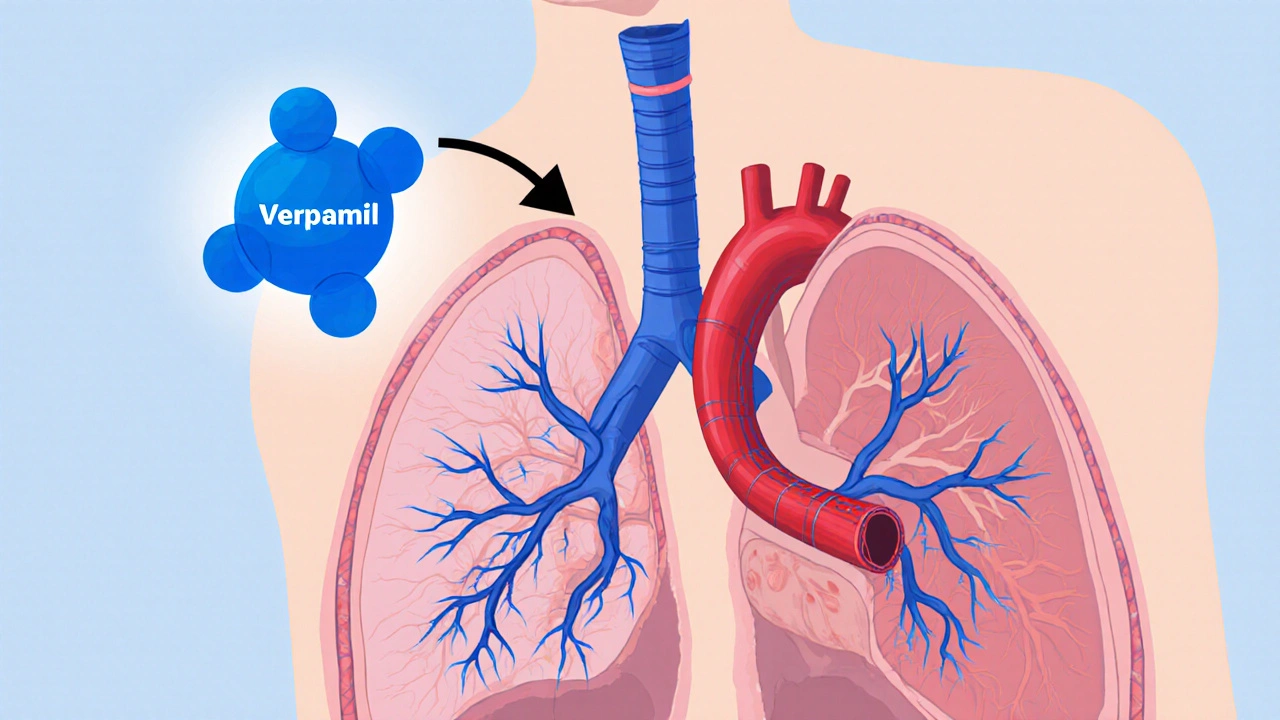
Explore how verapamil works for idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension, the evidence behind its use, patient selection, dosing, and future research.