When your body can’t make enough levodopa, a natural compound that the brain converts into dopamine. Also known as L-DOPA, it’s the cornerstone of treatment for Parkinson’s disease, a neurological disorder that breaks down movement control. Without enough dopamine, your brain struggles to send signals for smooth motion — leading to tremors, stiffness, and slow movements. Levodopa doesn’t cure Parkinson’s, but it’s the most reliable way to bring back some of that lost function.
Levodopa doesn’t work alone. It’s almost always paired with carbidopa, a drug that stops levodopa from breaking down before it reaches the brain. This combo means you need a lower dose, get fewer side effects like nausea, and get more of the drug where it’s needed. Think of carbidopa as a bodyguard — it keeps levodopa from getting wasted in your stomach and intestines. Without it, levodopa would be mostly useless, and you’d feel sick before you felt better.
Levodopa helps with motor symptoms, like shaking, slowness, and rigidity, but it doesn’t fix everything. Balance issues, speech problems, and cognitive changes often need other strategies. Over time, the effects can become less steady — you might notice your symptoms come and go between doses. This is called wearing off, and it’s why doctors adjust timing, add other meds, or sometimes switch delivery methods like patches or infusions.
It’s not a one-size-fits-all drug. Some people do great for years. Others notice side effects like dizziness, hallucinations, or odd movements (dyskinesia) after a while. What works for one person might not work for another. That’s why tracking your symptoms and talking regularly with your doctor matters more than just taking the pill.
The posts below cover real-world details you won’t find in brochures: how levodopa interacts with other meds, what to do when it stops working as well, how diet affects absorption, and how it compares to newer treatments. You’ll also find guides on managing side effects, understanding dosage timing, and avoiding dangerous combinations — especially with things like iron supplements or certain antibiotics. This isn’t theory. It’s what people actually deal with when they’re on levodopa every day.
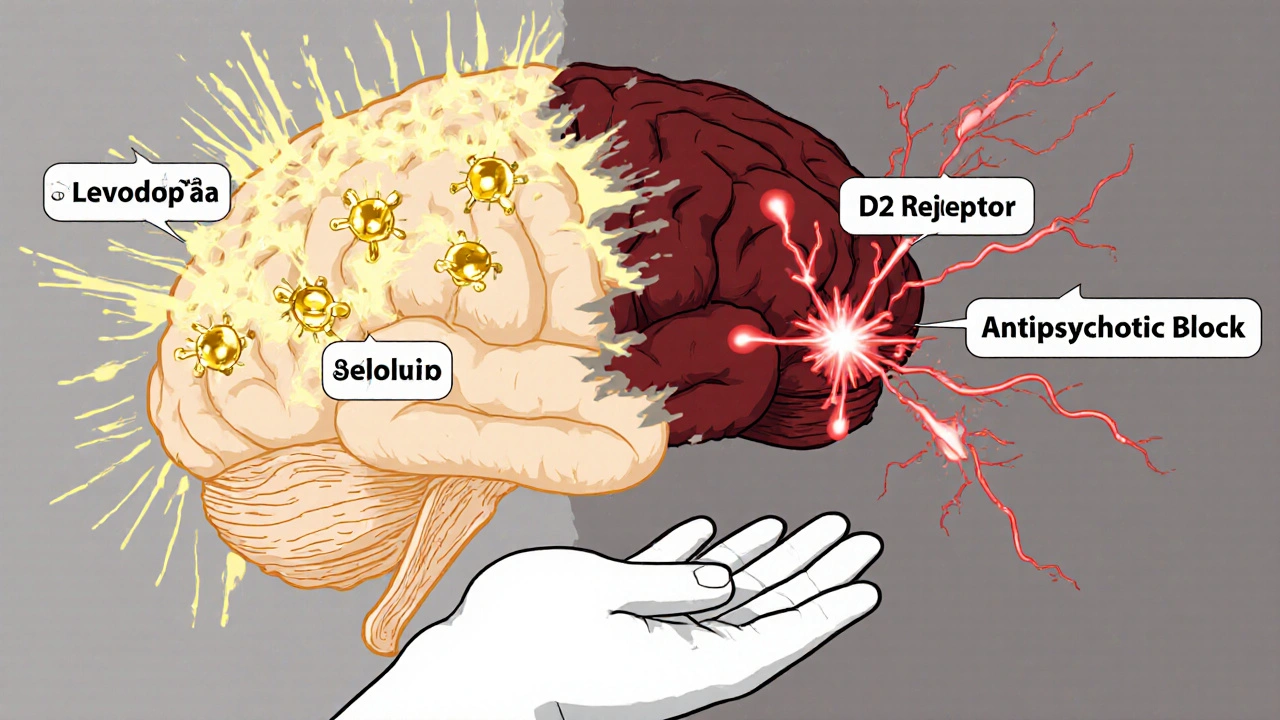
Levodopa and antipsychotics have opposing effects on dopamine, making it dangerous to use them together. This interaction can worsen Parkinson's symptoms or trigger psychosis, creating a difficult treatment dilemma for patients and doctors.