If you or someone you care about has IBD (Crohn’s disease or ulcerative colitis), the day-to-day can feel unpredictable. This tag page collects clear, practical articles about IBD treatments, common medications, cost-saving options, and how to safely use online pharmacies or telehealth services. Read on for quick, useful steps you can take now.
Doctors usually start with anti-inflammatories like mesalamine (5-ASA) or sulfasalazine for mild cases. If inflammation flares, short courses of corticosteroids such as prednisone can calm things down fast but aren’t for long-term use. For moderate to severe IBD, immunomodulators (azathioprine, 6-MP) or biologics (infliximab, adalimumab, vedolizumab, ustekinumab) are common. Each drug class has trade-offs: effectiveness, side effects, and monitoring needs. Talk to your gastroenterologist about goals—symptom control or deep remission—and what suits your life and health history.
Simple steps help more than you might expect. Track triggers (specific foods, stress, lack of sleep) in a notebook or a phone app. Stay hydrated and eat smaller, regular meals when flares hit. If diarrhea is a problem, low-fiber or BRAT-style meals can ease the gut temporarily. If pain or nausea is severe, call your provider—don’t guess with extra meds. For sleep and itch or skin issues that sometimes come with immune conditions, look at targeted tips in our dermatitis and sleep post.
Medication costs and access matter. We have hands-on guides comparing discount programs (GoodRx, InsideRx, Optum Perks) and telehealth services (Maple vs Felix) so you can find the fastest appointment and best price. If you order online, read our articles on safe pharmacies and RX alternatives—check licensing, clear contact info, and valid prescriptions before you buy.
Supplements and alternative ideas pop up everywhere. Some people try probiotics, vitamin D, or omega-3s; others look at herbal or seaweed supplements like Laminaria. These can help some people but aren’t replacements for prescribed IBD drugs. Talk with your doctor before adding supplements—some interact with meds or change lab results.
When to get urgent help: heavy bleeding, severe abdominal pain, high fever, fainting, or dehydration. Those are reasons to get emergency care. For ongoing care, establish a plan with your GI doctor: who to call, which tests to repeat, and when to consider stepping up therapy.
On this tag page you’ll find deeper articles on specific drugs, safety checks for online pharmacies, price-saving strategies, and newer treatment options. Use these resources to ask better questions at your next appointment and to find safer, cheaper ways to get the medicines you need.
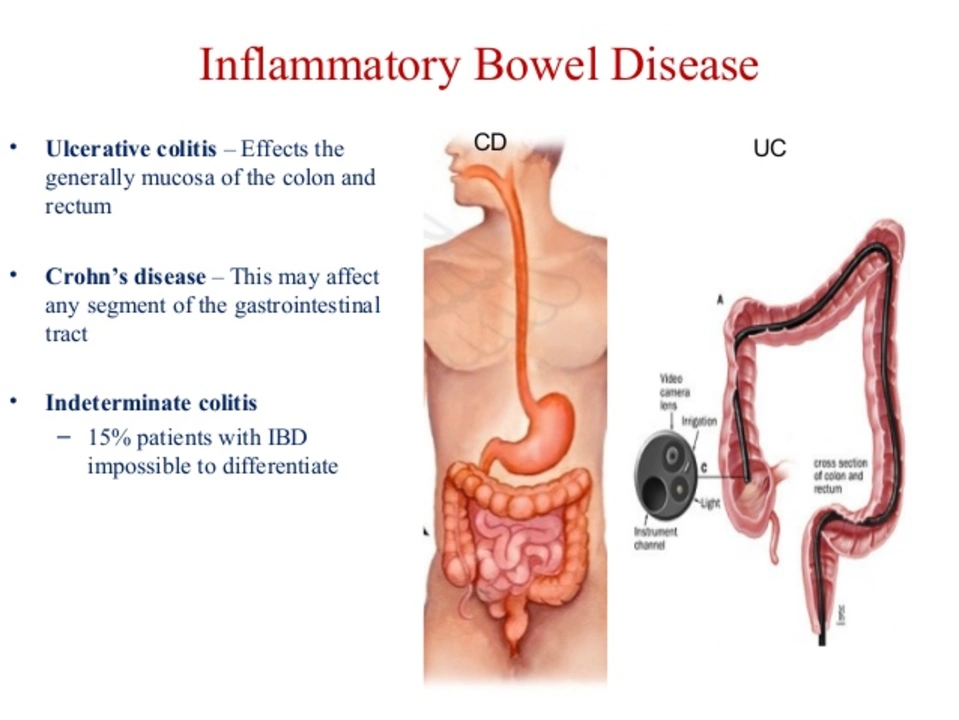
Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD) is a chronic condition that affects the digestive system and can significantly impact one's quality of life. Acotiamide, a gastrointestinal prokinetic drug, has recently emerged as a promising treatment option for managing IBD symptoms. Its role involves enhancing the movement of food through the digestive tract, thus alleviating discomfort and pain. I've noticed that patients taking Acotiamide have reported significant improvements in their symptoms, leading to a better overall quality of life. As a result, incorporating Acotiamide into IBD management plans could help many people regain control over their lives and enjoy a healthier, more comfortable existence.