Struggling with fullness, bloating, or discomfort after small meals? Acotiamide is a drug used to ease those symptoms in people with functional dyspepsia, especially the postprandial distress type. It’s best known in Japan (brand name Acofide) and has shown benefits for reducing early satiety and uncomfortable fullness.
Acotiamide helps the stomach move and relax more normally after eating. It boosts the signals that tell stomach muscles to contract and push food along. That means less bloating, less early fullness, and fewer unpleasant post-meal symptoms for many people.
Doctors usually consider acotiamide when lifestyle changes and basic treatments (diet tweaks, avoiding late big meals, or simple antacids) don’t help. People with clear signs of organic disease—like unexplained weight loss, bleeding, or severe vomiting—need tests first. Acotiamide is aimed at functional dyspepsia, not structural problems.
Typical dose used in trials is 100 mg taken three times a day before meals. Many people notice improvement within 2–4 weeks, though some need longer. Don’t expect instant relief after the first dose; give the course a few weeks unless side effects appear.
Common side effects reported are mild headaches and diarrhea. Serious reactions are rare, but stop the drug and call your doctor if you get severe stomach pain, yellowing of the skin or eyes, or signs of an allergic reaction. If you have liver or kidney disease, are pregnant, or breastfeeding, talk to your doctor—data are limited in those groups.
Acotiamide can interact with other medicines that change gut movement or have anticholinergic effects. That may reduce how well it works or increase side effects. Always list current meds to your prescriber.
Availability varies by country. It’s approved and commonly used in Japan; in other places it may be available only through clinical trials or not at all. If you’re curious, ask your doctor about access and alternatives like other prokinetics, dietary changes, or referral to a gastroenterologist.
Want to try acotiamide? Bring a clear symptom diary to your appointment: note when symptoms happen, foods that trigger them, and any past treatments. That helps your clinician decide if acotiamide fits your situation and how long to try it.
If symptoms worsen or new concerning signs appear, seek medical attention. For most people with functional dyspepsia, acotiamide is another reasonable option to discuss with a doctor when simple measures don’t cut it.
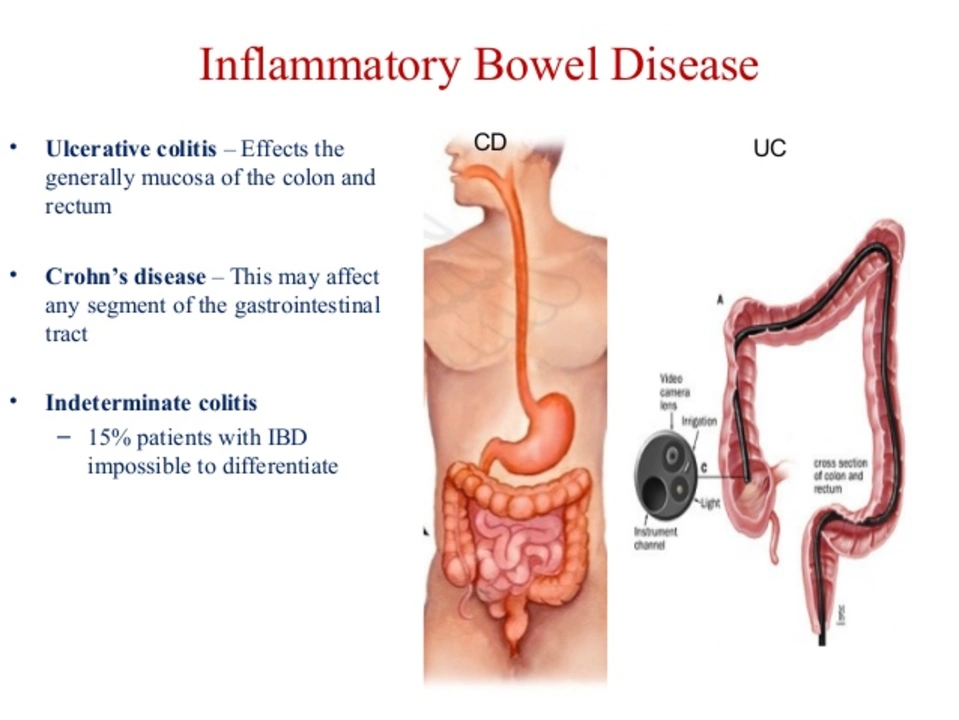
Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD) is a chronic condition that affects the digestive system and can significantly impact one's quality of life. Acotiamide, a gastrointestinal prokinetic drug, has recently emerged as a promising treatment option for managing IBD symptoms. Its role involves enhancing the movement of food through the digestive tract, thus alleviating discomfort and pain. I've noticed that patients taking Acotiamide have reported significant improvements in their symptoms, leading to a better overall quality of life. As a result, incorporating Acotiamide into IBD management plans could help many people regain control over their lives and enjoy a healthier, more comfortable existence.