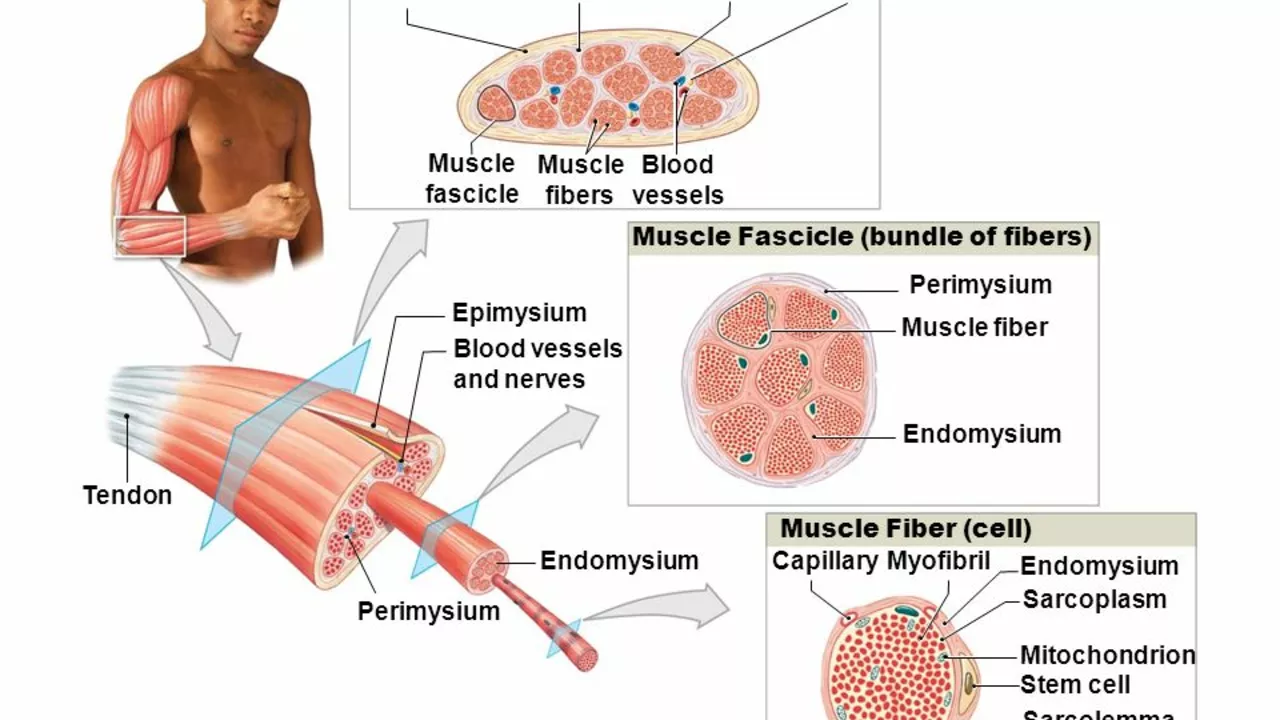
Understanding the Aging Process and Skeletal Muscles
As we age, our bodies undergo numerous changes, many of which are quite visible. However, some of the most significant changes happen internally, particularly within our skeletal muscles. Skeletal muscles are crucial as they support movement and balance. They are also responsible for our metabolic rate and body temperature regulation. As we grow older, these muscles tend to lose their strength and flexibility, which can significantly affect our quality of life.
Understanding the aging process and its effects on our skeletal muscles is essential for maintaining our health and independence as we age. It's not about reversing the aging process; it's about managing it effectively. This section seeks to provide a broad understanding of this complex process to provide a basis for the discussion on how aging affects skeletal muscles.
Age-Related Changes in Muscle Mass and Strength
One of the most noticeable effects of aging on skeletal muscles is the change in muscle mass and strength. This phenomenon, known as sarcopenia, starts as early as your 30s. Sarcopenia can lead to decreased strength and mobility, making daily activities more difficult to perform.
Sarcopenia is not just about losing muscle mass; it's also about losing muscle quality. As we age, the composition of our muscles changes. They become infiltrated with fat and connective tissue, which can further decrease strength and functionality. Understanding these changes can help us develop strategies to slow down this process and maintain our muscle health.
Impact of Aging on Muscle Performance
Without a doubt, aging affects muscle performance. You might find it harder to carry heavy groceries or climb stairs as you grow older. This is a direct result of the loss of muscle strength and power. But it's not just about strength. Muscles also lose their endurance, meaning that you might feel tired more quickly during physical activities.
Another critical aspect of muscle performance is speed. With age, our muscles respond slower, which can affect balance and increase the risk of falls. Understanding these changes is essential to adapt our lifestyles and exercise routines to maintain our muscle performance and overall health.
The Role of Exercise in Counteracting Muscle Aging
While we can't stop the aging process, we can certainly slow it down. And one of the most effective ways to do this is through regular exercise. Exercise not only helps maintain muscle mass and strength, but it also improves muscle quality, endurance, and speed.
Sure, you might not be able to lift as heavy weights or run as fast as you did in your 20s, but that doesn't mean you should stop exercising. The key is to adapt your exercise routine to your current abilities and gradually increase the intensity as your strength and endurance improve. Remember, it's never too late to start exercising, and every little bit counts.
Understanding and Managing Age-Related Muscle Pain
As we age, we might also experience more muscle pain. This is often a result of the wear and tear of our muscles and joints over the years. However, it can also be a sign of more serious conditions, such as arthritis or fibromyalgia.
Understanding the causes of muscle pain and learning how to manage it can greatly improve our quality of life as we age. This might involve a combination of medication, physical therapy, massage, and lifestyle changes. Remember, it's essential to consult with a healthcare professional if you're experiencing chronic or severe muscle pain.
In conclusion, aging does have a significant impact on our skeletal muscles, but that doesn't mean we can't do anything about it. By understanding these changes and adopting healthy habits, we can keep our muscles strong and functional, ensuring a better quality of life as we age.

Brittany McGuigan
July 26, 2023 AT 18:46In the U.S. we see a lot of folks skippng the gym once they hit the mid‑40s, but that is a serious mistake. Muscle loss isn’t just about looking good, it directly impacts our ability to stay independent, especially in a country that values self‑sufficiency. The article correctly points out sarcopenia starting in the 30s, yet many Americans ignore the early signs until they can’t lift a grocery bag. If you’re serious about keeping your strength, start resistance training now, not later. And remember, a strong body reflects a strong nation.
Priya Vadivel
July 26, 2023 AT 20:10Indeed, the physiological changes are unavoidable, however, as you mentioned, they are mitigated by consistent effort, especially with a balanced diet, proper rest, and a variety of exercises, each targeting different muscle fibers, and by staying socially active, which also influences hormonal balance, overall mood, and motivation, making the whole process more sustainable.
Dharmraj Kevat
July 26, 2023 AT 21:33Aging hits the muscles like a silent thief.
Lindy Fujimoto
July 26, 2023 AT 22:56Let me break it down for everyone, because clarity is essential when discussing something as crucial as muscle health💪. First, the infiltration of fat into muscle tissue isn’t just a cosmetic issue; it actively reduces contractile efficiency, leading to slower movement and higher fatigue rates. Second, the loss of fast‑twitch fibers means that our reflexes and power‑dependent tasks, like climbing stairs or catching a dropped object, become jeopardized, increasing fall risk. Third, consistent resistance training stimulates myogenesis, which counteracts sarcopenia by promoting satellite cell activation and protein synthesis. Fourth, nutrition plays an equally vital role; adequate protein intake, especially leucine‑rich sources, fuels muscle repair and growth. Fifth, sleep quality cannot be ignored-growth hormone peaks during deep sleep, and any disruption hampers recovery. Sixth, staying hydrated maintains intracellular volume, essential for optimal muscle function. Seventh, incorporating balance and flexibility drills reduces the likelihood of injury, as joints become more stable. Eighth, progressive overload is key-gradually increasing weight or resistance ensures continual adaptation, preventing plateaus. Ninth, mind‑muscle connection enhances neuromuscular recruitment, making each contraction more effective. Tenth, monitoring progress through simple metrics, like grip strength or a timed sit‑to‑stand test, provides feedback and motivation. Eleventh, genetic predisposition does influence baseline muscle mass, but lifestyle choices can offset many of those limitations. Twelfth, chronic inflammation from poor diet or inactivity accelerates muscle catabolism, so anti‑inflammatory foods are beneficial. Thirteenth, social support, whether from a workout buddy or a community group, improves adherence to exercise routines. Fourteenth, mental health directly impacts physical performance; stress hormones like cortisol can degrade muscle protein if chronic. Finally, never underestimate the power of consistency-small, daily actions accumulate into significant, lifelong benefits. So, whether you’re in your 20s or your 70s, the message is clear: move, lift, eat well, rest, and stay engaged. 🌟
darren coen
July 27, 2023 AT 00:20Consistency beats intensity. Small daily habits keep muscles active. Rest days prevent overtraining.